During postpartum pelvic floor examinations, novice mothers often ask: "I felt a piece of meat from the vaginal opening, and I always feel something is there. Is it prolapsed?"
"When urinating, there is a piece of meat in the vaginal opening, is it uterine prolapse?" Many novice mothers will diagnose vaginal wall bulge during the 42-day postpartum recheck and need pelvic floor rehabilitation training.
What is vaginal wall protruding?
Vaginal wall protruding refers to the protruding of the bladder, urethra, rectum and anus due to the failure of the pelvic floor muscles, fascia and uterine ligaments to return to their normal positions and protruding toward the vagina, which is exposed outside the vaginal opening. It is a type of pelvic organ prolapse.
Vaginal wall bulge is divided into anterior vaginal wall bulge (bladder/urethral bulge) and posterior vaginal wall bulge (rectocele). According to statistics, the incidence of vaginal wall bulging in postpartum women is as high as 40%, which is often accompanied by symptoms such as urinary incontinence and sexual discomfort.
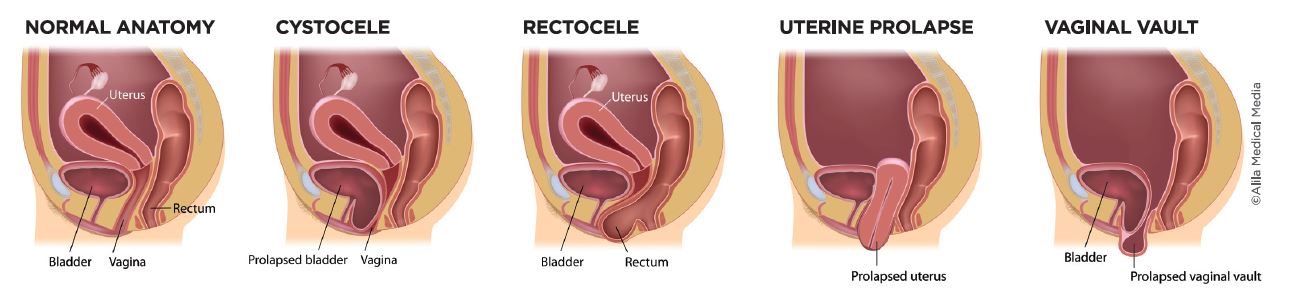
Why does the vaginal wall bulge?
Pregnancy and childbirth are the main reasons that affect the function of pelvic floor and vaginal support tissues. The enlarged baby, placenta, and amniotic fluid during pregnancy make the abdominal pressure more and more, the pelvic floor muscles are in a state of continuous stretching, the elasticity decreases, and the muscle strength is correspondingly weakened, which affects the pelvic and abdominal organs (bladder, urethra, uterus, rectum, etc.) , the supporting effect is significantly weakened.
Therefore, as the belly gets bigger and bigger during pregnancy, the abdominal pressure increases, and the pelvic floor muscles continue to be compressed. Some pregnant women have introitus enlarged during pregnancy and the vaginal wall protrudes outside the introitus. Some pregnant women may even have severe uterine prolapse.
In the prolonged second stage, the pubic bone, bladder, cervix, fascia and ligaments are overstretched and torn due to excessive compression during the partition, resulting in pelvic floor ligament and fascia relaxation, insufficient suspension force, and damage to the pelvic floor muscles Heavier, the ability to support and support pelvic organs also weakens.
If you do not recover in time after childbirth, resulting in pelvic instability, poor wound healing, scar adhesion or pain symptoms, vaginal wounds or cesarean section wounds cannot be effectively recovered, pelvic floor muscle contraction is asymmetrical, and pelvic and abdominal dynamics are not coordinated. Many pregnant women The bladder or rectum is prone to displacement, and the phenomenon of oppressing the vagina to bulge out of the vagina.
In addition, elderly women are also at high risk of vaginal bulging. As age increases, the level of estrogen decreases, pelvic floor muscle strength decreases accordingly, and the incidence of pelvic organ prolapse increases significantly. Chronic low back pain, scoliosis, pelvic instability, etc. can also cause asymmetrical contraction of the pelvic floor muscles, uncoordinated pelvic and abdominal dynamics, and pelvic organ prolapse. Therefore, whether pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation is done after childbirth has a direct impact on elderly urinary incontinence, vaginal wall bulging, and uterine prolapse. Therefore, mothers must not ignore postpartum recovery.
How to judge if you have a bulging vagina?
If you want to self-check whether the vagina is bulging, you can try to squat down, hold your breath, press down (as hard as you have a child), and feel for any protruding flesh from the vaginal opening? If you feel abnormal, it is best to go to the hospital immediately See a doctor for an examination. The doctor will perform related examinations based on your symptoms and medical history to confirm whether you have a vaginal bulge.
How to treat already suffering from vaginal bulge?
How to treat depends on the degree of impact of vaginal bulging on life:
▲Non-surgical treatment is usually used for patients whose occurrence time is not long and has little impact on life;
▲Surgical treatment can be adopted for pelvic organs that are obviously protruding from the vagina, which seriously affects life.
1. Non-surgical treatment
Non-surgical treatment generally includes pelvic floor rehabilitation (Kegel exercise), electrical stimulation and biofeedback therapy. Pelvic floor fascia manipulation therapy is also a very effective treatment method for mild to moderate pelvic organ prolapse.
According to research, electrical stimulation and biofeedback therapy have obvious effects on pelvic floor muscle repair. Kegel exercise is suitable for patients with degree I and degree II, but the wrong method will increase abdominal pressure and aggravate the damage to pelvic floor function. Therefore, it is necessary to coordinate pelvic and abdominal dynamics under the professional guidance of a doctor to perform relatively accurate Kegel training.
2. Surgical treatment
For patients whose vaginal wall bulges severely beyond the vaginal orifice, or even with severe uterine prolapse, surgical treatment can be considered according to their own conditions. Common surgical treatment methods include anterior/posterior vaginal wall repair, vaginal closure, and pelvic floor reconstruction.
What should be paid attention to in daily life?
The continuous increase in abdominal pressure is equivalent to worsening the pelvic floor muscles and fascia that have not been restored after delivery, and once again damages the pelvic floor muscles, resulting in a decrease in support for pelvic organs, and bulging and prolapse also occur.
1. Control abdominal pressure
For women with vaginal bulging, it is necessary to always pay attention to control abdominal pressure:
Avoid sitting for a long time, squatting for a long time, holding the child for a long time, etc.;
Avoid running, jumping, sit-ups and other sports;
Drink water and urinate regularly, and do not hold back urine;
People with constipation, be careful not to defecate too hard, and do not go to the toilet for too long;
Keep doing pelvic floor muscle exercises;
Try to minimize squatting to bathe your baby.
2. Do not use the postpartum restraint belt lightly
Many mothers want to lose weight quickly after giving birth and use restraint belts, but long-term use of restraint belts after childbirth will bring many adverse effects:
First, it will lead to poor discharge of postpartum lochia, affect pelvic blood circulation, cause gynecological inflammation, pelvic congestion syndrome, etc.;
On the other hand, a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen will also affect gastrointestinal motility, digestion, and severely cause pelvic organ prolapse, including uterine prolapse and bulging of the front and back walls of the vagina.

3. Exercise and repair core strength as soon as possible after delivery
The inner core includes the diaphragm, transversus abdominis, internal oblique, multifidus and so on. The recovery of postpartum pelvic floor strength is inseparable from the inner core condition. In fact, many women generally regard vaginal bulge, uterine prolapse, urinary incontinence, etc. as personal privacy issues, and either endure it or think that these conditions are very normal after giving birth. Generally, the symptoms of patients who go to the hospital for treatment are already very serious, and the course of treatment will be longer.
In fact, as long as attention is paid, early inspection, simple exercises and preventive measures can be used for good treatment. However, there is a "golden time" for preventive treatment. Generally, within one year after childbirth, it is best to perform recovery training of the pelvic floor muscles as soon as possible after the discharge of lochia on the 42 days postpartum. If there is no exercise and rehabilitation of pelvic floor muscles after childbirth, as the age increases and hormone levels decrease, menopause around the age of 50 will be a high incidence of urinary incontinence and prolapse.
2022-06-29
2022-06-16
2022-05-24
2022-04-28
2022-04-18
2022-03-17
2022-03-16
2022-03-14
2022-02-15
2022-01-21